
Epicureanism was a philosophical doctrine formulated by the Greek philosopher, Epicurus. According to his teachings, you can achieve the highest good in life only through pleasure and avoidance of pain.
What is Epicureanism?
SUMMARY
Epicureanism is a philosophy that suggests that you can have a good life only through pleasure and avoidance of pain.
“It is impossible to live a pleasant life without living wisely and well and justly, and it is impossible to live wisely and well and justly without living a pleasant life.”
—Epicurus
The ancient philosophical school founded by the Greek philosopher Epicurus (341 – 270 BCE) is referred to as Epicureanism. This system of philosophy started to challenge Platonism. Later on, its chief opponent was Stoicism. This concept became popular in the late Hellenistic period and also during the reign of the Roman emperors.
The main teachings of Epicureanism were that pleasure brought the most good in life. So, our main purpose in life should be the pursuit of pleasure. Epicureanism ethics is based on a set of hedonistic values. The principal objective of this philosophy was related to pleasure and pain. Seek the greatest pleasure and avoid pain at all costs.
Therefore, according to this philosophical teaching, a person would get the greatest pleasure when he could completely remove all kinds of physical and mental pain.
Epicurean definition
A person who practices the Epicureanism philosophy is called an Epicurean.
Let us study the definitions of ‘Epicurean’ as given by the best dictionaries.
• In the Oxford Learner’s Dictionaries, Epicurean is “taking great pleasure in things, especially food and drink, and enjoying yourself.”
• Cambridge Dictionary suggests the following definition for Epicurean –
“getting pleasure from food and drink of high quality.”
Merriam Webster has defined Epicurean “of or relating to Epicurus or Epicureanism.”
• According to Collins Dictionary, “devoted to sensual pleasures, esp food and drink; hedonistic.”
Epicureanism example
Most of the definitions provided in the modern popular dictionaries as we studied in the previous section are misinterpretations of Epicureanism. It is an ancient philosophy and most works of Epicurus have been lost. Although he had compiled hundreds of documents only a few Epicurus letters have been found.
His works had been described by his followers but still, a huge gap exists as to what he exactly taught to his disciples. The Lives and Opinions of Eminent Philosophers compiled by the biographer Diogenes Laërtius give some highlights on the life and principles of Epicurus. We also get an idea about Epicurean teachings in the book Letter to Menoeceus, which is a compilation of letters addressed to a student. Epicureanism can also be studied from Letter to Herodotus written by Epicurus. It is an introduction to his philosophy that was regarded as the “Little Epitome” by his students.
At this modern age, many will refer to living a luxurious life, eating good food and expensive wine, and having free sex as an Epicureanism example, but it’s not. Although Epicureanism is a form of hedonism, it did not suggest it’s followers to experience physical pleasures.
On the other hand, living a modest life with a lot of friends, doing self-reflection, staying in the present moment in absence of pain are examples of Epicureanism.
The Epicurean school of philosophy categorized pleasure into two separate groups –
1. pleasures of the body
2. pleasures of the mind
Epicurus believed that desire itself was painful. The greatest pleasure would come from the removal of all such physical and mental pleasures.
Further, Epicurus stated there are three kinds of human desires.
1. Natural and necessary
Food, shelter and clothing are examples of this first category.
2. Natural but not necessary
For instance, when you are hungry you will desire to eat some fine delicious food. It’s a natural desire but not necessary for you to have.
3. Not natural nor necessary
There are desires which are not innate to us. The desire for fame and prosperity, for example. These are desires that will never be satisfied. You will only need more of those.
According to Epicureanism, you just need to fulfill the first category of desires, the ones which are natural and necessary. Only then you will attain aponia and ataraxia that will give you the greatest happiness. The second and third category of desires will only bring you pain and dissatisfaction in life.
Epicureanism beliefs/lessons
Epicureanism advocated attaining the highest form of happiness and living a blissful life. Epicurus formed a community which he called Garden.
He bought this beautiful house with a garden far from the city and noise. It was a peaceful home where he lived with his friends cum followers. In this private space, he and his friends discussed ideas and spent time together.
Epicureanism was hugely popular in ancient Greece and also in the Roman Empire. It dominated for about 600 years! After that, it faded away with the surge of Christianity.
Here are the major beliefs of Epicureanism philosophy.
- Emphasize the pleasures of the mind and seek only the pleasures that are natural and necessary.
- Avoid all unnatural desires at all costs. Stay away from human affairs. Don’t participate in politics or the lust for power will take your peace of mind.
- Wanting to avoid pain and seeking pleasure is innate. However, by pain, Epicurus did not just indicate bodily pain. He suggested pain as any unpleasant negative sensation that affects our peace of mind.
- The Epicurean social contract is a “pledge of reciprocal usefulness neither to harm one another nor be harmed.”
- Don’t chase fame and wealth.
- Seek good and supportive friendships.
- Epicureans think most people hold this false belief that all sense-impressions are not true. Because Epicureans assume that all sense-impressions are indeed true.
- Belief in supernatural powers can bring fear, so eliminate such beliefs.
- Avoid entering into marriage or passionate love relationships or it will cause pain.
- The Epicurean philosopher said life is a “bitter gift.”
- Apply knowledge and reason while making decisions. It will lead to pleasure.
- Live simply and peacefully. Don’t keep fears and anxieties in your mind.
- Epicureanism believed in the concept of soul but they believed it was mortal just like our body.
- The concept of the afterlife was rejected in Epicureanism theory and it instructed to get rid of the fear of death. The Epicurean philosophy states that death has no sensation so there is no need to be scared of it. “Death is nothing to us; for that which is dissolved, is without sensation, and that which lacks sensation is nothing to us.”
Epicureanism incorporates some major philosophical doctrines:
• Metaphysics
Epicureanism believes in atomic theory. The world is made of atoms and it obeys the natural laws. There is nothing called afterlife.
• Theology
Gods exist. But they are not concerned about us. Hence, we should not bother about them. The fear of the gods must be removed.
• Epistemology
The greatest truth prevails in how the human mind senses the world.
Epicureanism vs stoicism
There are some major differences between these two age-old philosophical schools. You can also draw a few similarities between the two concepts.
Let’s compare the two schools of thoughts. There must be some invaluable insights in both of these philosophies or why did they gain so much of public attention? Why are these philosophical doctrines still talked about so much?
Let us learn the similarities and differences between the principal doctrines of the two schools.
Similarities – Epicureanism and Stoicism
1. Both are Hellenistic philosophy that originated in Athens, Greece.
2. Epicureanism suggests leading a simplistic life with friends while the Stoic perspective is accepting life as it comes. Therefore, both of these schools offer ways to avoid pain in life for the highest good.
3. Epicureanism and stoicism, both warned against living an excessively pleasure-driven life.
4. Both philosophies aim at living a good life.
5. The Stoics view virtue as a major factor in life. The Epicurean school also recognizes virtue as a useful way of living a pleasant life.
Differences – Epicureanism and stoicism
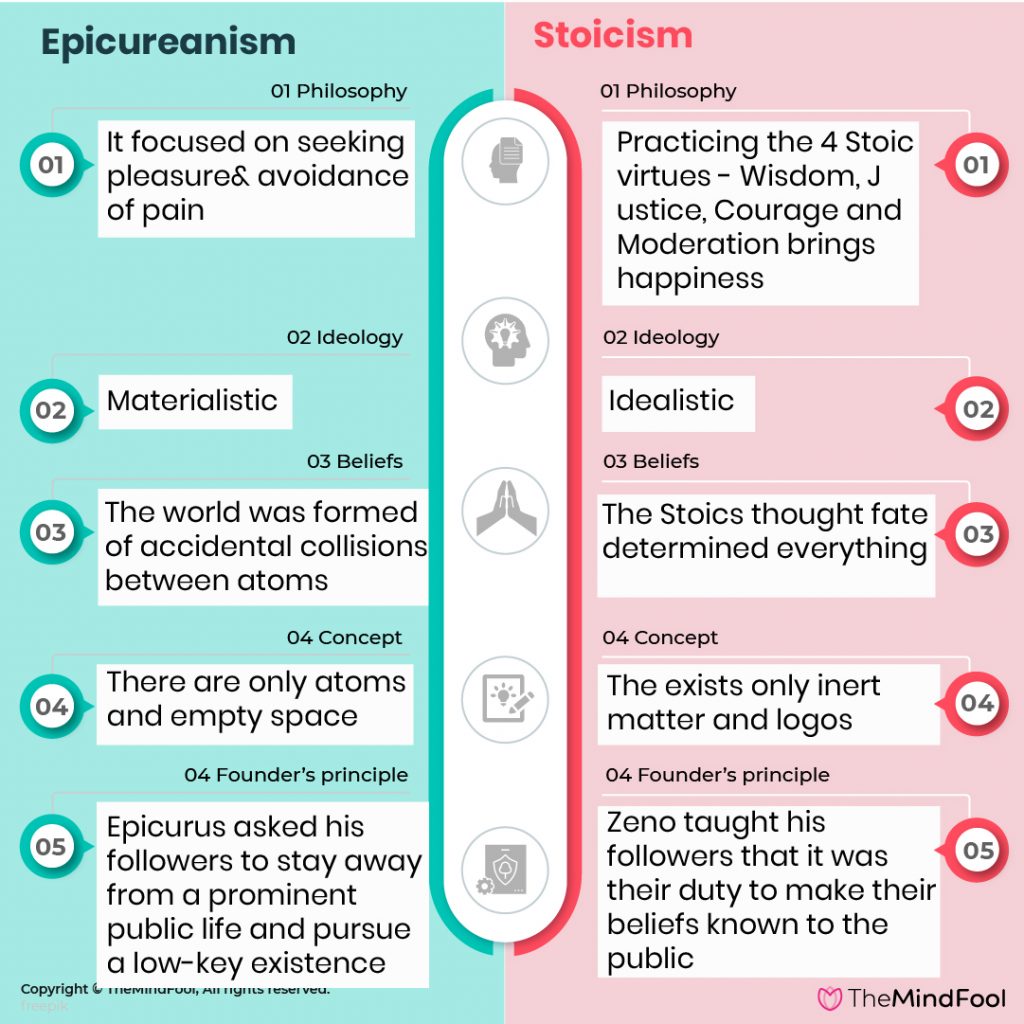
| Epicureanism | Stoicism | |
| Founder | Epicurus of Samos | Zeno of Citium |
| Philosophy | It focused on seeking pleasure and avoidance of pain | Practicing the 4 Stoic virtues – Wisdom, Justice, Courage and Moderation brings happiness |
| Ideology | Materialistic | Idealistic |
| Beliefs | The world was formed of accidental collisions between atoms | The Stoics thought fate determined everything |
| Concept | There are only atoms and empty space | The exists only inert matter and logos (reason) |
| Founder’s principle | Epicurus asked his followers to stay away from a prominent public life and pursue a low-key existence | Zeno taught his followers that it was their duty to make their beliefs known to the public |
NOTE
Stoicism turned to be a chief opponent of Epicureanism. Both of these schools of thoughts received huge popularity. They also had to face a lot of criticisms.
Closing Thoughts
The ancient school of Greek philosophy started by Epicurus advocated living a life where pleasure was the greatest source of happiness. However, Epicureanism did not propose receiving physical pleasure. Rather, the idea was to gain mental pleasure through simple living, valuable friendships, and avoidance of pain. To live happily you must get rid of all sources of fear, stress, and anxiety and open the doors to true mental happiness.
Ishita is a published author, poet and freelance writer. Being an avid reader from early childhood, she has always loved books more than anything else in the world! At the start of her career, she has worked in the corporate as well as the academic sector being a double master's degree holder - M.Sc and MBA. But now she is a fulltime writer. She believes words have immense power and writers can make a huge impact in the world! She wants to bring positivity into the lives of the readers through her association with TheMindFool.
